The Blockchain Identity Paradigm Change
During our analysis, some have suggested that the above (enterprise) ID lifecycle is not representative of how blockchain can transform Identity. They have subsequently called for a new paradigm.
According to Kaliya “Identity Woman” Young: “The mental models of how identity is “managed” whether by an employer relative to an employee or by a government relative to a citizen or by an individual just logging into to a web service is disrupted by the new emerging standards of DIDs and Verifiable Credentials.
In the classic identity management lifecycle an individual establishes an account (enrollment) with an organization and then returns to use that account (doing authentication to prove they are the owner). The establish many different accounts all in this same manner and with a user-name and password.
The individual gets an account with an organization. This happens dozens if not 100’s of times at a variety of different services.
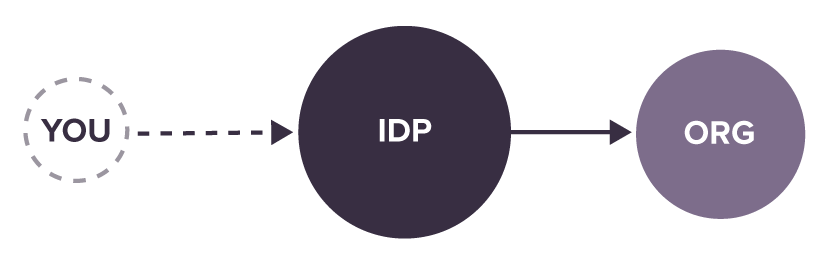
If they want to prove things about themselves from one service to another in a digital way they have to connect with another service an identity or attribute provider to retrieve the attributes. This means that the two services have to have a technical and also likely a business relationship. It creates a privacy challenges and technical complexity.
There is also the emergence in the consumer space of Mega IDPs such as Google and Facebook that sit in the middle between the individual and many of the the services and organizations they log in to. They have a account within the name space of that IdP and it can be terminated by them, individuals have almost no recourse when this happens.
Systems like India’s Aadhaar and the Estonia eID system have the government in the role of Mega Identity provider seeing all the places that one uses the digital identity issued by the government to the citizen.
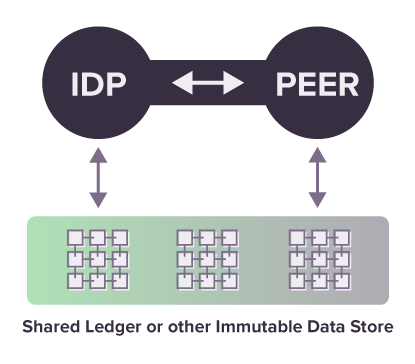
With Decentralized Identity the paradigms change completely. The individual has the capacity to stand on their own with an identifier (DID) they created and control completely.
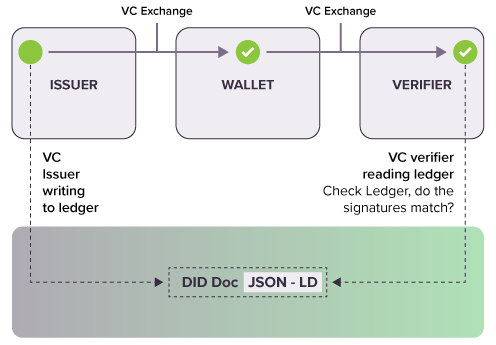
The other thing that changes with this new technology is ability to share credentials from what used to be called an “identity provider” and this new paradigm is called the issuer with what used to be called a “relying party” and now is called the verifier. Blockchain technology provides a way issue credentials to the individual in a digital wallet under their control and present the claims to whatever verifier they choose. The Verifier and the Issuer never actually communicate electronically and they do not have to have a business or technical relationship.”